
He called these small pieces of matter “ atomos”, in Greek it means indivisible.ĭemocritus stated that atoms were specific to the material which they composed. And after that, he tried to cut the stone continually into smaller and smaller pieces up to some point where there would be a piece that would be so small as to be indivisible. At that time, Democritus found that if a stone was divided in half, the two halves would have essentially the same properties as the whole. He spent the last years of his life working and publishing papers.The first atomic theorist was Democritus, a Greek scientist and philosopher who lived in the fifth century BC.

Schrödinger spent the last years of his working career in Dublin. However, because he had left Germany, he was seen as an enemy. Schrödinger returned to his native country for a little while after he was offered a post at University of Graz. He had an Oxford University Fellowship for a while and received an offer from Princeton University. That same year, Hitler came to power in Germany and Schrödinger decided that it was time to go to England. He won the Nobel Prize in 1933 with Paul A.M Dirac. The move turned out to be a wonderful one for him. Despite making some great strides in his career, Schrödinger was hesitant to take the offer at first, uneasy about moving to a big city from the picturesque Alps. He moved to Berlin in 1972 to take on the post. Schrödinger was offered the prestigious position of Max Planck, a physicists who had already changed the way people thought about the field with his groundbreaking theories on quantum dynamics and thermal radiation. In his later years, he produced interesting philosophical questions related to the field of mathematics and physics. Schrodinger’s equation is part of his enduring legacy when it comes to technical contributions to the field. However, the physicist himself put a stop to this rift when he proved that both were identical, simply expressed in different ways. Unlike Heisenberg’s, Schrödinger’s theory could be visualized. The academic world was chiefly divided between two publications, Schrödinger’s own and that of Werner Heisenberg. His idea in the publication quickly became known by the name Schrödinger’s Wave Equation. This is when the physicist started to explore the idea of a wave when it comes to the movement of an electron in an atom. During this time, he read a footnote in one of Albert Einstein‘s works which sparked his interest in wave mechanics.
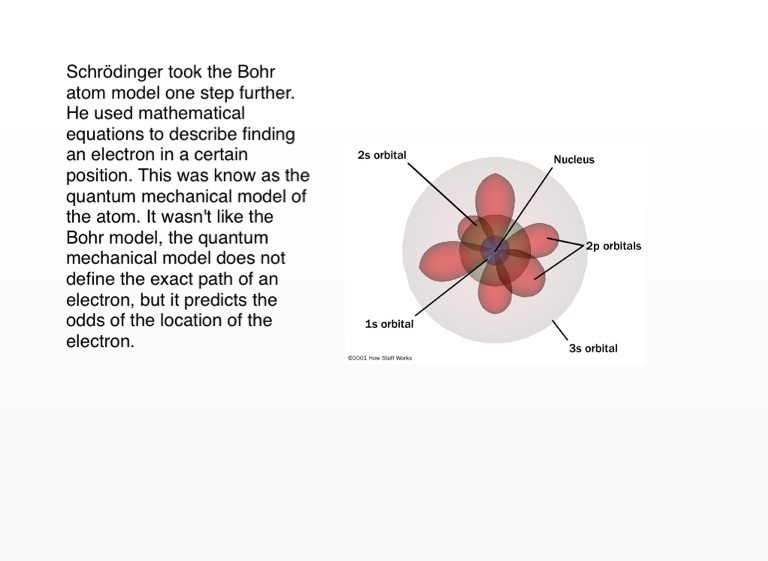
This was the most productive point of his career. ZurichĪfter getting married and moving from one position to another, Schrödinger was recruited to be the head of the physics department at the University of Zurich in Switzerland. When Schrödinger went up to receive the Nobel Prize in 1933, he said that if it was not for the war, his mentor would have been the one to receive the honor. Schrödinger was in the Italian artillery during World War I. After Schrödinger received his PhD he became part of the faculty at the University of Vienna. The work he did with his mentor during this time in his career would turn out to be the foundation to a great deal of his later work. Once he started studying at the university, he came under the influence of Friedrich Hasenhörl.

He dabbled in botany and painting when he was a young man. He was a highly educated man and the only son of parents that valued education. Famous For: Schrodinger equation, Schrodinger’s cat, Schrodinger method, Schrodinger functional, Schrodinger group, Schrodinger picture, Schrodinger-Newton equations, Schrodinger field, Rayleigh-Schrodinger perturbation, Schrodinger logics and Cat stateĪwards: Nobel Prize in Physics (1933) and Max Planck Medal (1937)Įrwin Schrödinger was a famous Austrian theoretical physicist that contributed to our current understanding of physics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
